Differetiable Simulators
Overview
- DiffSim: a scalable C++ framework for differentiable physics that can support a large number of rigid and deformable objects and their interactions.
- FluidLab: a fully differentiable and multi-material physics simulation platform, supporting rigid, elastic, plastic materials, inviscid and viscous liquid, and gaseous phenomena such as smoke.
- PlasticineLab: a differentiable soft-body manipulation simulator and benchmark.
- DiffArticulated: a differentiable simulation system for articulated rigid bodies.
- DiSECt: a differentiable simulation engine for autonomous robotic cutting.
- ThinShellLab: a differentiable simulator for manipulating thin-shell materials, such as cloths and papers.
- DaxBench: a deformable object manipulation benchmark with differentiable physics.
- NimblePhysics: a general purpose differentiable physics engine for articulated rigid bodies.
- MuJoCo XLA(MJX): a re-implementation of the MuJoCo physics engine in JAX, which is differentiable.
- SoftMAC: a differentiable soft body simulation with forecast-based contact model, coupling with articulated rigid bodies and clothes.
DiffSim
DiffSim is a scalable C++ framework for differentiable physics that can support a large number of rigid and deformable objects and their interactions.
Details
DiffSim: Scalable Differentiable Physics for Learning and Control
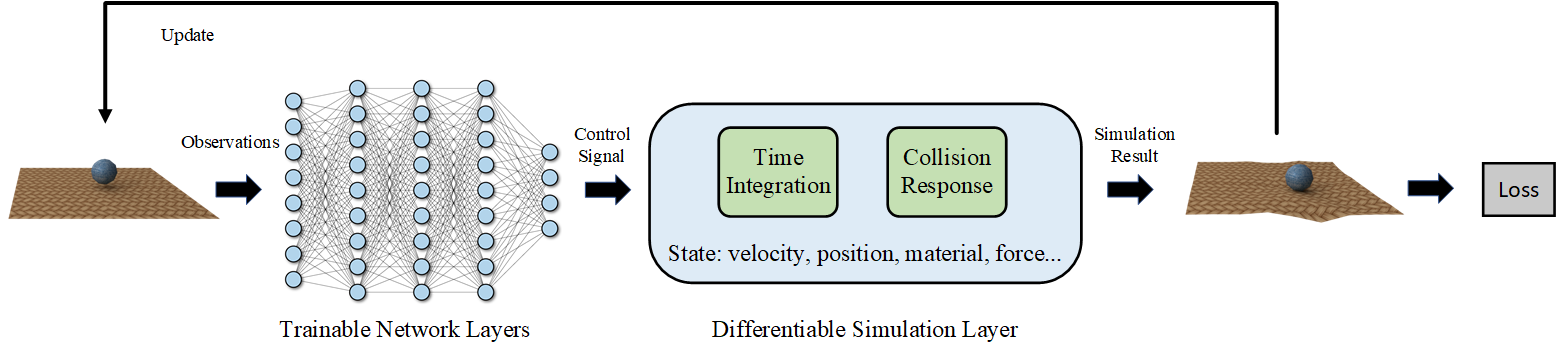
DiffSim is a scalable framework for differentiable physics that can support a large number of objects and their interactions. It adopts meshes as its representation and leverage the sparsity of contacts for scalable differentiable collision handling. Collisions are resolved in localized regions to minimize the number of optimization variables even when the number of simulated objects is high. It further accelerates implicit differentiation of optimization with nonlinear constraints. DiffSim requires up to two orders of magnitude less memory and computation in comparison to contemporary particle-based methods.
FluidLab
FluidLab and FluidEngine is a fully differentiable and multi-material physics simulation platform, supporting rigid, elastic, plastic materials, inviscid and viscous liquid, and gaseous phenomena such as smoke.
Details
FluidLab: A Differentiable Environment for Benchmarking Complex Fluid Manipulation
FluidLab is a simulation environment with a diverse set of manipulation tasks involving complex fluid dynamics. These tasks address interactions between solid and fluid as well as among multiple fluids. FluidLab is powered by its underlying physics engine, FluidEngine, providing GPU-accelerated simulations and gradient calculations for various material types and their couplings, extending the scope of the existing differentiable simulation engines.
PlasticineLab
PlasticineLab is a differentiable soft-body manipulation simulator and benchmark.
Details
PlasticineLab: A Soft-Body Manipulation Benchmark with Differentiable Physics
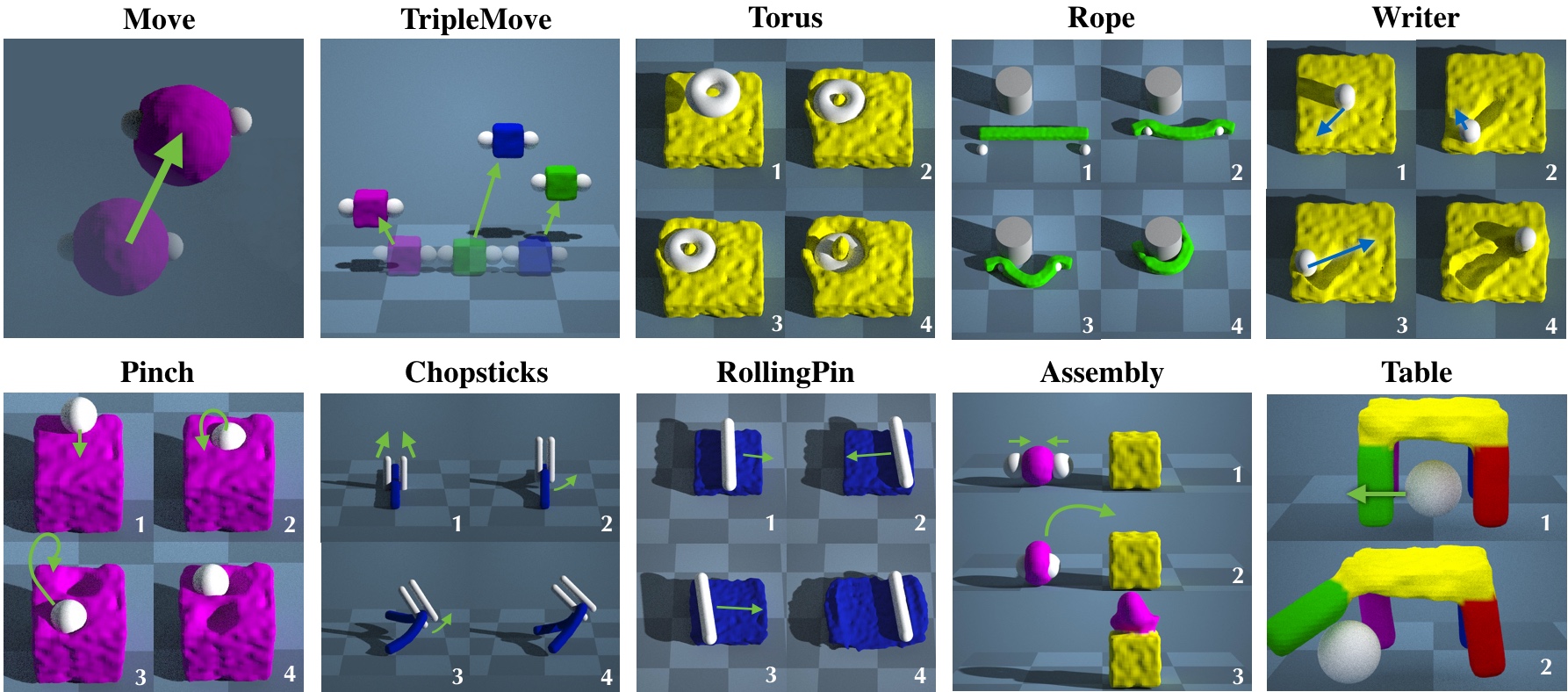
DiffArticulated
DiffArticulated is a differentiable simulation system for articulated rigid bodies.
Details
DiffArticulated: Efficient Differentiable Simulation of Articulated Bodies

DiffArticulated is a method for efficient differentiable simulation of articulated bodies. This enables integration of articulated body dynamics into deep learning frameworks, and gradient-based optimization of neural networks that operate on articulated bodies. The gradients of the contact solver are derived using spatial algebra and the adjoint method, resulting in simulation speed that's an order of magnitude faster than autodiff tools.
DiSECt
DiSECt is a differentiable simulation engine for autonomous robotic cutting.
Details
DiSECt
DiSECt is a simulator for the cutting of deformable materials. It uses the Finite Element Method (FEM) to simulate the deformation of the material, and leverages a virtual node algorithm to introduce springs between the two halves of the mesh being cut. These cutting springs are weakened in proportion to the knife forces acting on the material, yielding a continuous model of deformation and crack propagation. By leveraging source code transformation, the back-end of DiSECt automatically generates CUDA-accelerated kernels for the forward simulation and the gradients of the simulation inputs. Such gradient information can be used to optimize the simulation parameters to achieve accurate knife force predictions, optimize cutting actions, and more.
ThinShellLab
ThinShellLab is a differentiable simulator for manipulating thin-shell materials, such as cloths and papers.
Details
ThinShellLab: Thin-shell Object Manipulations with Differentiable Physics Simulations
ThinShellLab is a fully differentiable simulation platform tailored for robotic interactions with diverse thin-shell materials possessing varying material properties, enabling flexible thin-shell manipulation skill learning and evaluation. This comprehensive endeavor encompasses a triad of experiment task categories, which are as follows: manipulation tasks, inverse design tasks, and real-world experiments.DaxBench
DaxBench is a deformable object manipulation benchmark with differentiable physics.
Details
DaxBench: Benchmarking Deformable Object Manipulation with Differentiable Physics


NimblePhysics
NimbelPhysics is a general purpose differentiable physics engine for articulated rigid bodies.
Details
NimblePhysics
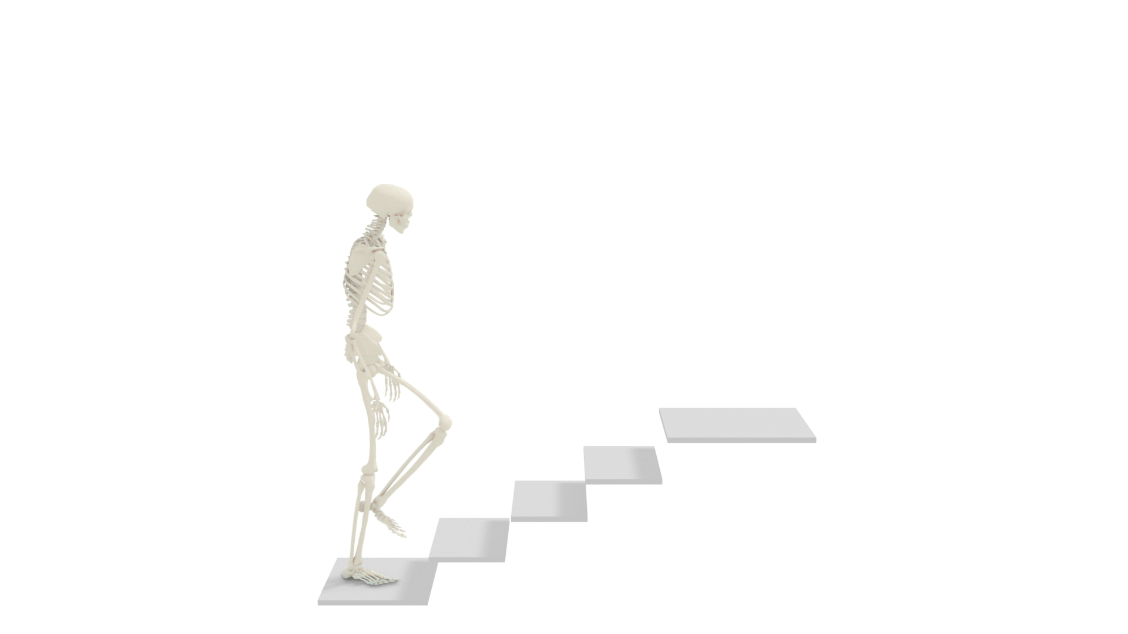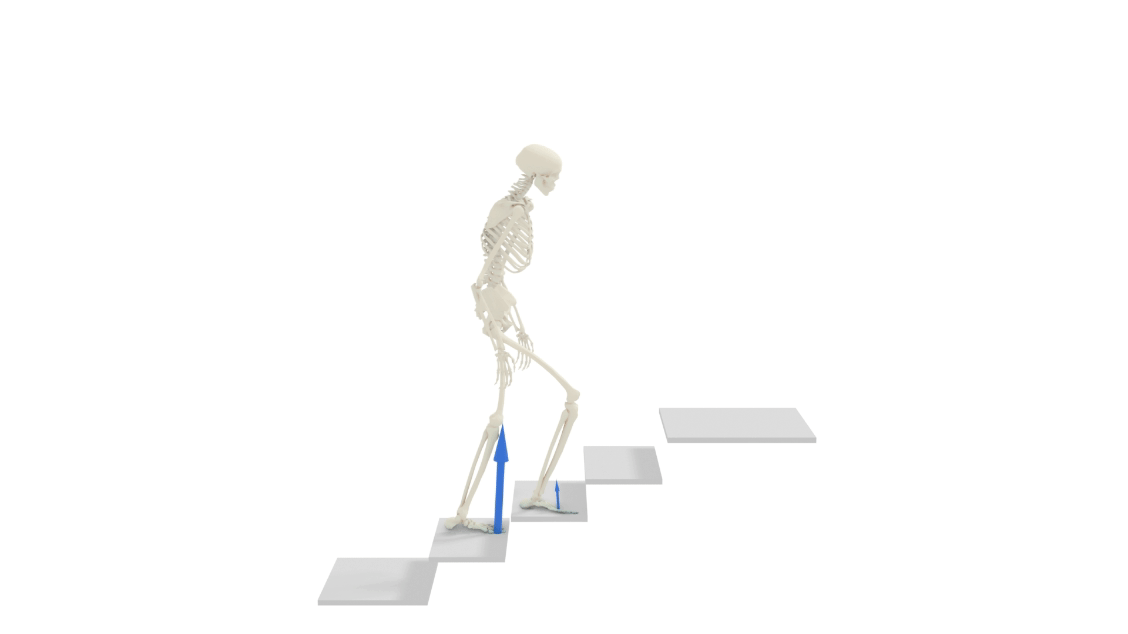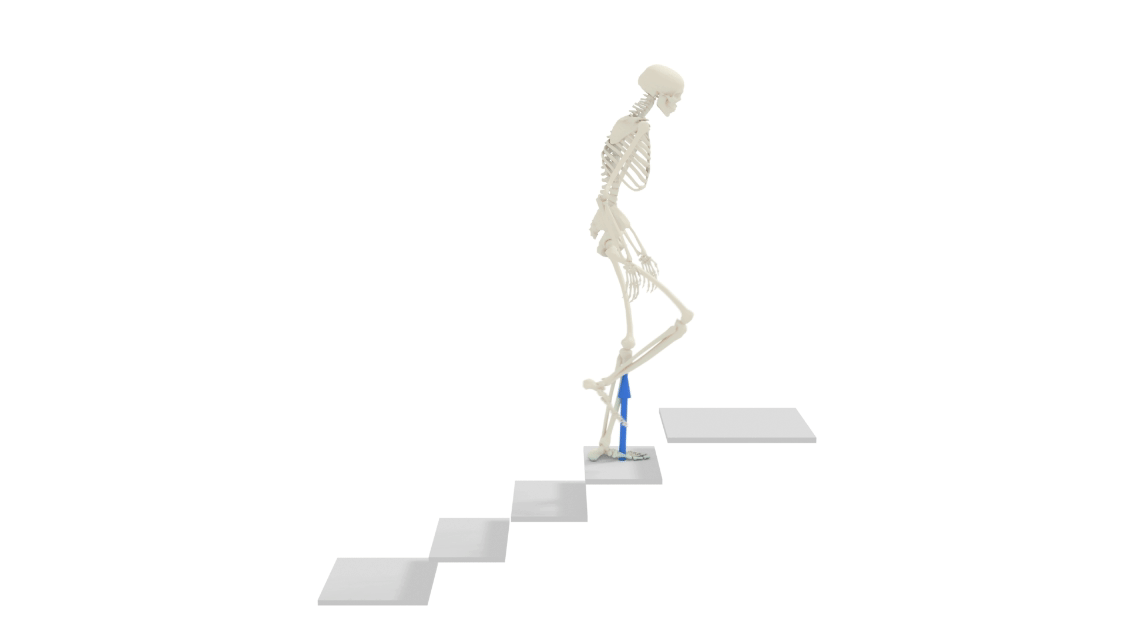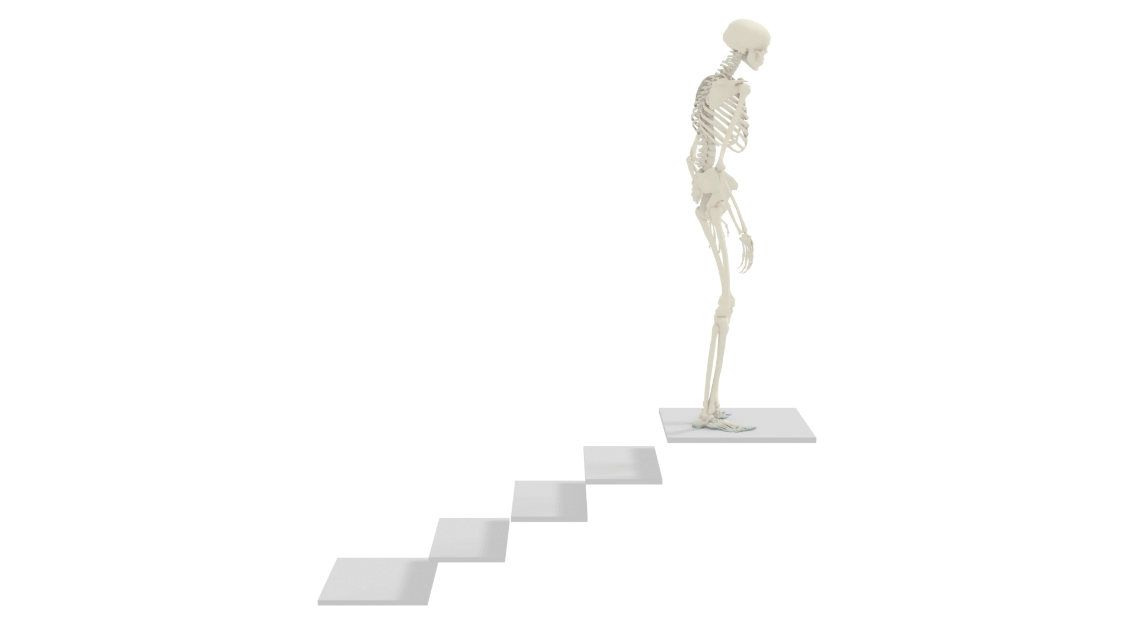
Nimble is a toolkit for doing AI on human biomechanics (physically simulated realistic human bodies), written in C++ for speed, but with nice Python bindings. It focuses on studying real physical human bodies. Nimble started life as a general purpose differentiable physics engine, as a fork of the (not differentiable) DART physics engine.
MJX
MuJoCo XLA(MJX) is a re-implementation of the MuJoCo physics engine in JAX.
Details
MuJoCo XLA(MJX)
Starting with version 3.0.0, MuJoCo includes MuJoCo XLA (MJX) under the mjx directory. MJX allows MuJoCo to run on compute hardware supported by the XLA compiler via the JAX framework. MJX runs on a all platforms supported by JAX: Nvidia and AMD GPUs, Apple Silicon, and Google Cloud TPUs. The MJX API is consistent with the main simulation functions in the MuJoCo API.
SoftMac
SoftMac is a differentiable soft body simulation with forecast-based contact model, coupling with articulated rigid bodies and clothes.









-purple)



